Blelloch Scan in OpenCL
Blelloch Scan
Background
Scan(Exclusive Scan)是说, 对于一个序列:,我想要得到:
串行版本很简单,时间复杂度和工作量都是
void Scan(
const std::vector<int>& input,
std::vector<int>& output
) {
output.at(0) = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < input.size(); i++) {
output.at(i) = input.at(i) + input.at(i-1);
}
}
Blelloch Scan是一种work-efficient的GPU上的Scan的实现, 根据这里的介绍, Blelloch Scan的好处是它所需要的工作量和串行的版本差不多,渐进(asymptotically)都是. 但是相比于串行版本很难理解。
分为两个阶段:
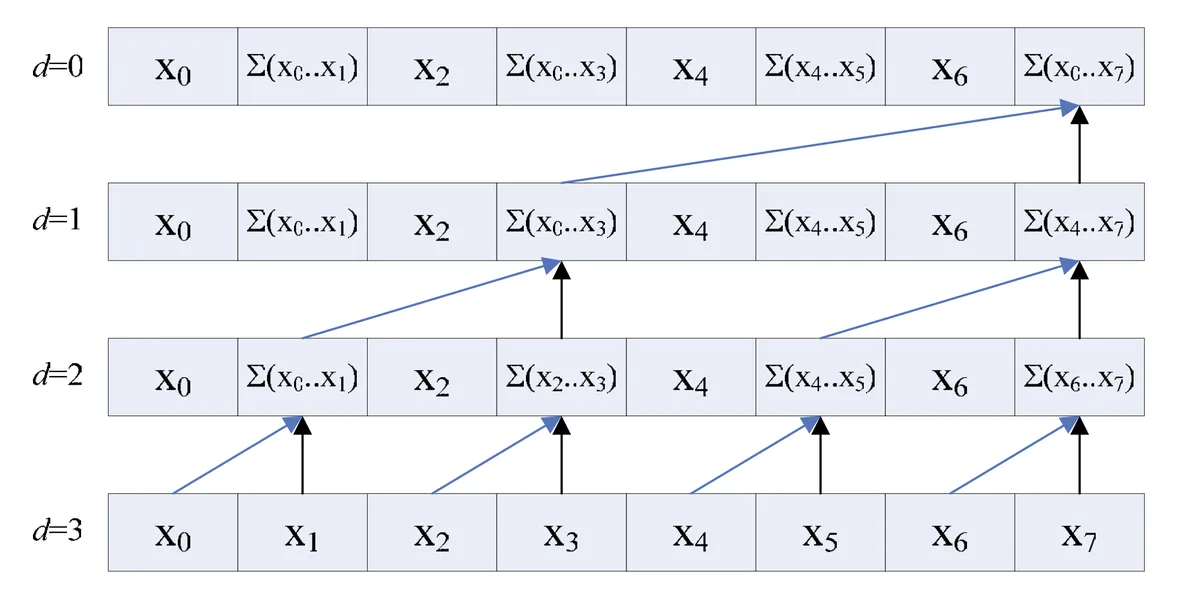
Up-sweep (Reduction)
感觉叫做UpSweep是因为这个步骤是从输入的一个个单独的元素,两两一组作为逻辑上的二叉树的两个子节点,把sum的值传递给父节点。
for to do
for all to by in parallel do
Up-sweep阶段,父子节点其实是前后步骤之间,序列中某个元素如何变化的关系,将两个元素(左右子节点)的sum存储到父节点。
同时也可以发现:
- Up-sweep阶段在的步骤,不会最大化利用尽可能多的线程
- Up-sweep的工作量是
Down-sweep
Down-sweep阶段反过来,我们这里实现的是exclusive scan,所以把根节点存储的值设为0,这个值会传递下去加到每一个元素上。
for down to do
for to by in parallel do
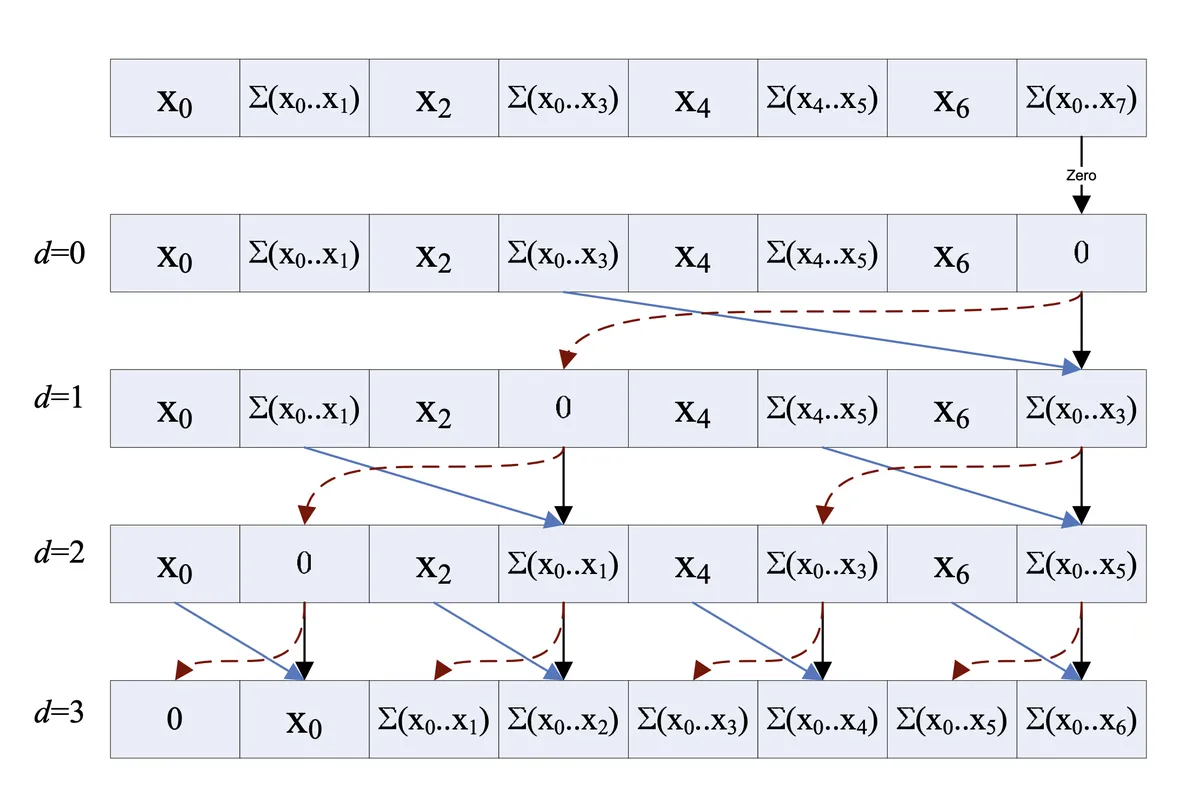
对于upsweep阶段,我的理解是,upsweep阶段得到的每个节点的左孩子存储了左子树的区间和,例如的左子树的范围是, 那左孩子存储的值是,这张图里面我用绿色全部标记了出来。
如何把upsweep的结果,转化成prefix-sum呢?需要在down-sweep阶段:
- 从根节点一层一层一直到叶子节点
- 每一层都将父节点的值——也就是已经算的部分前缀和,传到左节点,
- 每一层都将父节点的值——也就是已经计算的部分前缀和,加上右节点的左兄弟的值——也就是父节点的左子树的区间和。
进行到叶子节点就还原了整个数组的前缀和。 感觉太烧脑了,只有画图才能够明白这个步骤。
Blelloch在Introduction to Parallel Algorithms的4.1节给出了一个递归形式算法的证明,我们上面描述的是迭代的,所以只能参考一下,不过对于理解左子树,右子树的操作的含义很有帮助。
OpenCL Implementation
计算一个tile的prefix-sum
这是一个tile内的数组的Blelloch Scan的实现,加了详细的注释,包括每一步的中间结果,每一个步骤用了几个thread。
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// This kernel performs an exclusive prefix sum (also known as scan)
// on a block of data using Blelloch's algorithm (work-efficient scan)
//
// Each work-group operates on a tile of data independently,
// using local memory as a scratch space for summation magic.
// Results are written back to global memory, and optionally,
// the total sum of each tile can be stored in `tile_sums`.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
__kernel void scan(
__global int* data, // Input/output array in global memory
__global int* tile_sums, // Optional output of per-tile total sums
__local int* temp, // Local scratch space for scan
const int N // Total number of elemenets
){
// Identify this thread's global and local position
int gid = get_global_id(0); // Absolute position in the global arena
int lid = get_local_id(0); // Position inside the current work-group
int group = get_group_id(0); // Which work-group this is
int lsize = get_local_size(0); // The size of this work-group
// Out-of-bounds check: do not process data beyond the end
if (gid >= N) return;
// Phase 1: Load data into the shared local memory
temp[lid] = data[gid];
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE); // Wait for all threads to complete load
// Phase 2: Up-sweep (Reduction)
// Accmulate values in a binary tree fashion
// index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// temp: [a0][a1][a2][a3][a4][a5][a6][a7]
//
// offset = 1:
// [a0][a0+a1][a2][a2+a3][a4][a4+a5][a6][a6+a7]
// => temp[1] += temp[0]
// => temp[3] += temp[2]
// => temp[5] += temp[4]
// => temp[7] += temp[6]
//
// offset = 2:
// [a0][a0+a1][a2][a0+a1+a2+a3][a4][a4+a5][a6][a4+a5+a6+a7]
// => temp[3] += temp[1]
// => temp[7] += temp[5]
//
// offset = 4:
// [a0][a0+a1][a2][a0+a1+a2+a3][a4][a4+a5][a6][a0+a1+a2+a3+a4+a5+a6+a7]
// => temp[7] += temp[3]
// Now temp[7] holds the total sum
for (int offset = 1; offset < lsize; offset <<=1) { // from leaf to root
int index = (lid + 1) * offset * 2 - 1;
if (index < lsize) {
temp[index] += temp[index - offset];
}
// Because some thread use other thread's result in formor steps
// we need to sync after each step, prevent race condition
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
}
// Phase 3: Prepare for exclusive scan
// set last element to 0 for exclusive scan
if (lid == lsize - 1) {
if (tile_sums != NULL) {
// Save total sum of this tile
tile_sums[group] = temp[lid];
}
temp[lid] = 0;
}
// Sync before swap in Down-sweep Phase
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
// Phase 4: Down-sweep (Distribution)
// Traversing the tree backwards to build exclusive prefix sums
// Use local size of 7 for example:
//
// Initial:
// T7:
// temp[7] = 0
// step0 res: [a0] [a0+a1] [a2] [a0+a1+a2+a3] [a4] [a4+a5] [a6] [0]
//
// offset = 4, local_thread_index=0, temp_index=7
// T0:
// t = temp[3](a0+a1+a2+a3)
// temp[3] = temp[7](0)
// temp[7] = t(a0+a1+a2+a3) + temp[7](0)
// step1 res: [a0] [a0+a1] [a2] [0] [a4] [a4+a5] [a6] [a0+a1+a2+a3]
//
// offset = 2, local_thread_index=0,1, temp_index=3,7
// T0:
// t = temp[1](a0+a1)
// temp[1] = temp[3](0)
// temp[3] = t(a0+a1) + temp[3](0)
// T1:
// t = temp[5](a4+a5)
// temp[5] = temp[7](a0+a1+a2+a3)
// temp[7] = t(a4+a5) + temp[7](a0+a1+a2+a3)
// step2 res: [a0] [0] [a2] [a0+a1] [a4] [a0+a1+a2+a3] [a6] [a0+a1+a2+a3+a4+a5]
//
// offset = 1, local_thread_index=0,1,2,3, temp_index=1,3,5,7
// T0:
// t = temp[0](a0)
// temp[0] = temp[1](0)
// temp[1] = t(a0) + temp[1](0)
// T1:
// t = temp[2](a2)
// temp[2] = temp[3](a0+a1)
// temp[3] = t(a2) + temp[3](a0+a1)
// T2:
// t = temp[4](a4)
// temp[4] = temp[5](a0+a1+a2+a3)
// temp[5] = t(a4) + temp[5](a0+a1+a2+a3)
// T3:
// t = temp[6](a6)
// temp[6] = temp[7](a0+a1+a2+a3+a4+a5)
// temp[7] = t(a6) + temp[7](a0+a1+a2+a3+a4+a5)
// step3 res: [0] [a0] [a0+a1] [a0+a1+a2] [a0+a1+a2+a3] [a0+a1+a2+a3+a4] [a0+a1+a2+a3+a4+a5] [a0+a1+a2+a3+a4+a5+a6]
for (int offset = lsize >> 1; offset > 0; offset >>= 1) {
int index = (lid + 1) * offset * 2 - 1;
if (index < lsize) {
int t = temp[index - offset];
temp[index - offset] = temp[index];
temp[index] += t;
}
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
}
data[gid] = temp[lid];
}
首先需要将一个tile的数据加载到local memory,OpenCL中需要在加载local memory之后做一次同步,保证所有线程都加载完毕local memory。
down-sweep 和 up-sweep 的每一个步骤都需要做同步,因为后续的步骤需要用到上一步的结果。
TODO
上面只有一个tile的版本,一个数组分为多个tile分别计算,每个tile都有一个部分的sum,对每个tile的sum做prefix-sum能得到每个tile需要加上的offset,从而计算出最终完整数组的prefix-sum。
解决bank-conflict
github link
- https://github.com/utsusemioxo/two_stage_blur/tree/main/test_scan

